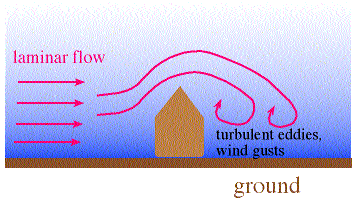
Friction in the Boundary Layer - eddy viscosity
Eddy viscosity refers to the internal friction generated as laminar (smooth, steady) flow becomes irregular and turbulent as it passes over irregularities on the surface (trees, buildings, mountains, etc)
Eddy motions created by obstructions are commonly referred to as mechanical turbulence
mechanical turbulence produces a frictional affect (drag) on the air flow that is much larger than caused by molecular viscosity
QUESTION FOR THOUGHT:
After a winter snowstorm, Cheyenne, Wyoming reports a total snow accumulation of 48 cm, while the maximum depth in the surrounding countryside is only 28 cm. If the storms intensity and duration were practically the same for a radius of 50 km around Cheyenne, explain why Cheyenne received so much more snow.