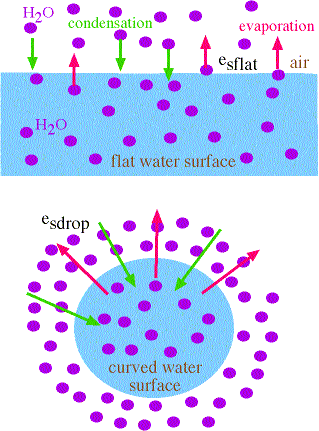
Flat versus Curved Water Surfaces
- given flat and curved water surfaces where the air adjacent to each is saturated -->>
- more energy is required to maintain the "curvature" of the drop
- therefore, the water molecules on the surface of the drop have more energy
- therefore, they evaporate more readily that from the flat water surface (compare the length of the red arrows)
- therefore: evaporation rate off curved surface > evaporation rate off of flat surface
- since air above both surfaces is saturated, then
- evaporation rate = condensation rate
- therefore, condensation rate onto droplet > condensation rate onto flat water surface
- therefore, esdrop > esflat
- therefore:
- if RHflat = 100%, then RHdrop > 100%
- the air surrounding the drop must be supersaturated!!
- This is called the curvature effect